Complément :
d'après Molecular Biology of the Cell the Problems book, 6th Edition - J.Wilson and T.Hunt
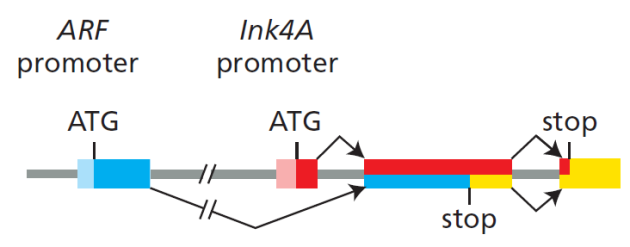
Le locus Ink4A-Arf code pour 2 protéines suppresseur de tumeur, Ink4A et Arf qui partagent un exon commun mais sont traduites selon différents cadres de lecture :
Mécanisme mis en jeu
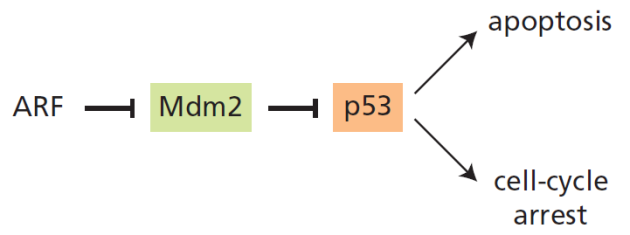
Des mutations dans les tumeurs humaines dont on pensait initialement qu'elles affectaient Ink4A ont été ultérieurement associées à une nouvelle protéine codée par un cadre de lecture différent (d'où le nom Arf pour Alternative reading frame). L'une des fonctions principales de Arf est d'inhiber Mdm2 qui est lui-même un inhibiteur du suppresseur de tumeur p53. La relation entre Arf, Mdm2 et p53 est représentée ci-dessous :
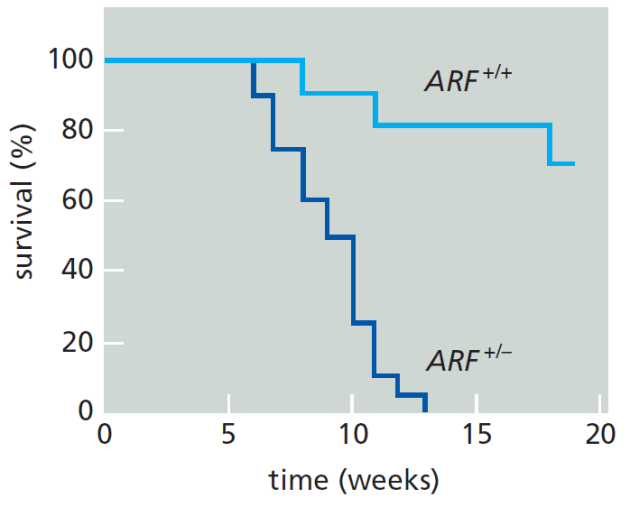
Souris KO Arf-/- et cancer
Souris p53+/+ Mdm2-/- et cancer
L'oncogène Myc, en plus de stimuler les voies de prolifération cellulaire, active également Arf. On étudie l'effet de l'expression de l'oncogène myc chez les souris en fonction de leur génotype (Arf+/+ ou Arf+/-)